Upon its entry into force, the Solvency II Directive included two review clauses:
- In 2018, for the sole delegated regulation (level 2).
- In 2020, for the directive (level 1) and the delegated regulation (level 2).
In December 2023, the Trilogue negotiations between the European Parliament, Commission and Council agreed on the review of Solvency II, allowing for the adoption of Level 1 amendments (the Directive). The European Commission then published draft Level 2 amendments (delegated acts) in July 2025, providing technical details to the directive. The Addactis experts offer you an analysis of the Pillar 1 major changes, definitely adopted at Level 1 and still draft at Level 2.
In this article, you will find these 5 key points:
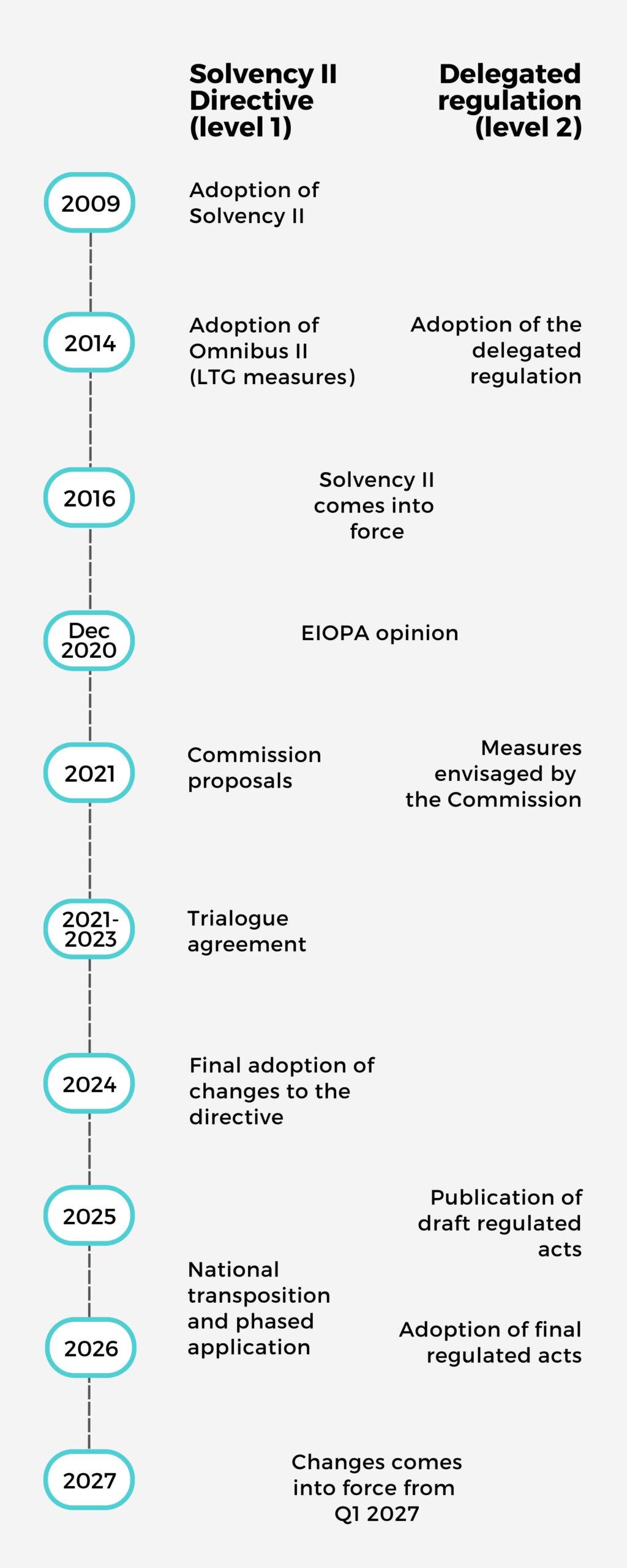
Legislative process for the 2020 Solvency II Review
In December 2023, the trilogue negotiations between the European Parliament, Commission and Council reached an agreement on the Solvency II Directive.
The reviewed directive was then formally adopted by MEPs in April 2024 and published in the Official Journal of the European Union (OJEU) in January 2025.
The amended directive entered into force 20 days after its publication and the measures will be applicable two years later, i.e. from 1 January 2027 for the first quarter of 2027 closings.
The European Commission has yet to adopt the amendments to the delegated acts. To this end, it published a draft text for consultation in July 2025.
Pillar 1 in the 2020 Solvency II Review: 6 Key Issues
Extrapolation of the Risk-Free Rate Curve
Objective: To take into account liquid market data beyond the first extrapolation point in order to benefit from an enhanced best estimate.
Themes:
- First Smoothing Point (FSP)
Replaces the current Last Liquid Point (LLP). It corresponds to the first maturity beyond which interest rates will start converging towards the UFR.
- Volatility Adjustment (VA)
Added on top of the extrapolated part of the curve (beyond the FSP).
- Convergence Parameter
The UFR weight should correspond to 77,5% of the extrapolated rates 40 years after the FSP as a minimum. According to the draft regulated acts, a new convergence formula for risk free rates towards the UFR with a convergence factor ”a” set at 11% for the Euro.
Volatility Adjustment
Objective: Redefine the VA to better mitigate the impact of observed spread movements on insurance liabilities.
Themes:
- Reference Portfolio Composition
Only composed of European debt instruments.
- Application Ratio
Increases from 65% to 85%.
- Sensitivity Ratio for assets and liabilities
Additional ratio specific to every undertaking to allow for differences in sensitivities between assets and liabilities, applied to the VA in addition to the application ratio.
- Macro-Economic VA
Will replace the actual national component with a correction factor linked to exposure specific to each country.
Risk Margin
Objective: To take into account the reduction of the correlation between risks throughout time and reduce sensitivity of the Risk Margin to interest rates variations.
Themes:
- Cost of Capital
New CoC fixed at 4,75% at level 1. The European Commission could review it at level 2 while staying in a 4% to 5% corridor.
- Introduction of a time-dependent parameter
This exponentially decreasing parameter λt aims at introducing a risk dependency evolution over time. Its value will drive the decreasing speed and will be confirmed at Level 2. The draft regulated acts propose a level of 0,96 for λ with a 50% minimum for λt
Standard Formula: Market SCR and correlations
Objective: to reduce the correlation between a reduction in interest rates and a change in credit spreads.
Themes: this correlation factor would go down from 50% et 25% in the draft regulated acts.
Standard Formula: Rate SCR
Objective: To better take into consideration the recent interest rate environment which could lead to an understatement of the SCR. Still at draft stage in the regulated acts.
Themes:
- Increased Capital Requirements relative to the interest rate shocks
Greater spread of both upward and downward shocks with the introduction of a shock on negative rates.
- Risk Correlation
Reduction in correlation between spread risk and interest rate down SCR from 50% to 25%.
- Transitional Phase
None.
Standard Formula: Equity SCR and symmetric adjustment
Objective: Provide room for manœuvre to undertakings so that they can contribute to the financing of real economy.
Themes:
- Criteria for the eligibility to Long-Term Equity Investments (LTEI)
Revised criteria to facilitate access to the derogatory prudential regime and expand the list of eligible assets. Reduction of minimum holding from 10 to 5 years.
- Equity risk sub-module based on duration
Removal of the sub-module.
- Equity Dampener
Increase the upper and lower bounds of the dampener from +/- 10% to +/- 13%, enhancing the counter-cyclical effect of the measure.
Solvency II review: anticipating the changes ahead
The ongoing Solvency II review is expected to result in significant changes for both L&H and P&C stakeholders (risk margin, interest rate SCR, LTEI, and equity dampener), and other focused on long-term guarantees (interest rate curve extrapolation and volatility adjustment).
Addactis experts are available to assist in understanding the technical issues, the different positions of co-legislators, and the potential implementation timeline.
Contact us to better understand how to tackle Solvency II challenges within your organisation.
This article is written by:

Antoine CHANH
Senior Manager – Modeling & Risk P&C

François BAYÉ
Head of Actuarial Consulting

Simon THIBAULT
Director – Modeling & Risk Life

Thibaut GILLIARD
Deputy Head of Modeling & Risk Health
Related articles on Solvency II
Solvency II: the Ultimate Forward Rate for 2026 by EIOPA
Solvency II – Ultimate Forward Rate (UFR) for 2026: Read our experts’ comments and analyses on EIOPA’s latest publication about UFR.

Risk-free rate curves and EIOPA data
Each month, Addactis lists and summarizes the economic parameters used to produce the solvency ratio and the economic balance sheet: risk-free rate curves, volatility correction, symmetrical equity adjustment, etc. Read our article now.

ORSA & Solvency II: turning compliance into strategic advantage
ORSA under Solvency II goes beyond compliance. It serves as a key driver of better governance, strategic planning and risk management.